Technology
Single Cell RNA-seq
Existing scRNA-seq technologies based on template-switching methods are widely used. However, these techniques have problems in the accurate evaluation of cell composition and the sensitivity of gene detection by the template-switching method.
The TAS-Seq method (Terminator-assisted solid-phase cDNA amplification and sequencing) uses a template-independent enzyme, terminal transferase (TdT), a ddNTP terminator terminator for TdT The combination of TdT, a template-independent enzyme, a stochastic stopping mechanism of the TdT reaction by a ddNTP terminator terminator, and microwell/magnetic bead-based cell isolation technology has been shown to detect more genes and highly-variable genes with higher sensitivity than existing methods, regardless of the amount of sequencing. The results of this study are as follows.
Accurate detection of cellular composition in tissue
Higher gene detection sensitivity
More robust
detection of intercellular communication
More robust
detection of growth factors, IL expression, etc.
Comparison of cell detection accuracy between flow cytometers and various techniques in mouse lung cells
Compared to flow cytometer data, TAS-seq correlates well with flow cytometers and provides accurate cell composition data.
10X v2 data from other methods over-detected macrophages and under-detected fibroblast fractions. (See red box)
Smart-seq2 data over-detected endothelial cells and monocytes and lost alveolar macrophages (see green box).
Shichino S. et al. Communications Biology volume 5, Article number: 602 (2022)
Detection of intercellular communication in mouse lung
Development of TAS-seq2
We have optimized the reaction system of TAS-Seq and developed TAS-Seq2 with even higher detection sensitivity.
Example of nuclear analysis of cells derived from mouse liver specimen using TAS-Seq2
*10X nuclear conditioning kit with anti-nuclear pore complex hashtags approx. 20000-30000 reads / nucleus
TAS-Seq2 enables more sensitive detection of genes in cell nuclei than other methods
10X v3.1: Published mouse liver sample data (SRX14774301, SRX14774300)
Multiplex Analysis
(Universal Surface Biotinylation : USB method)
Multiplex analysis is a technique that enables simultaneous analysis of multiple samples by using Tag antibodies or streptavidin with DNA barcodes on cells from different sample sources, called cell hashing. We use Universal Surface Biotinylation (USB), a universal labeling technology that does not depend on specific cell surface proteins.
Universal Surface Biotinylation: a simple, versatile and cost-effective sample multiplexing method for single-cell RNA-seq analysis
TCR Repatoir Analysis
High sensitivity, unbiased
By synthesizing cDNA from mRNA and amplifying the TCR gene with a common primer, IGT's amplification method is more sensitive and unbiased than systems that start with cDNA and amplify the variable region with multiple primers. Moreover, the TCR gene expression level of quiescent T cells is low (a few copies per cell), and repertoireanalysis requires high detection sensitivity. IGT's amplification method is one of the most sensitive among existing technologies.
Duplicate clonal analysis of tumor-infiltrating T cells
CD4/CD8 repertoire analysis in cancer tissue:
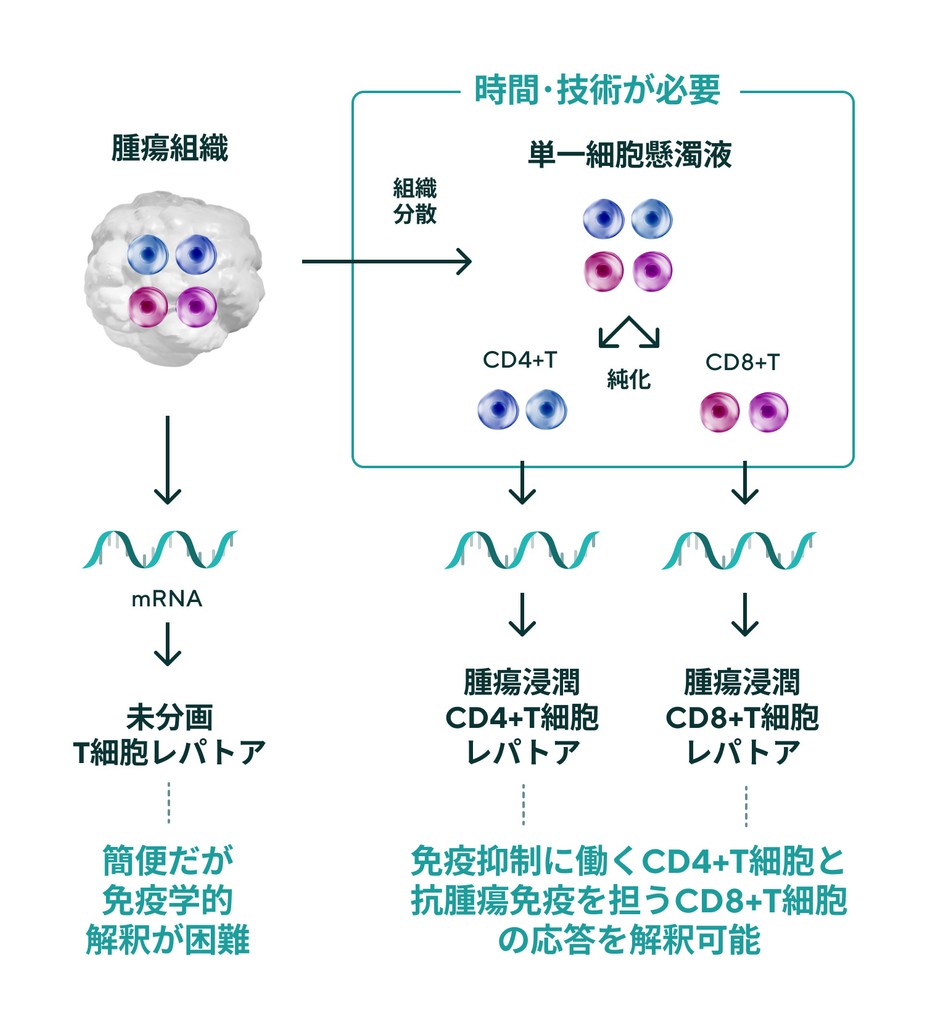
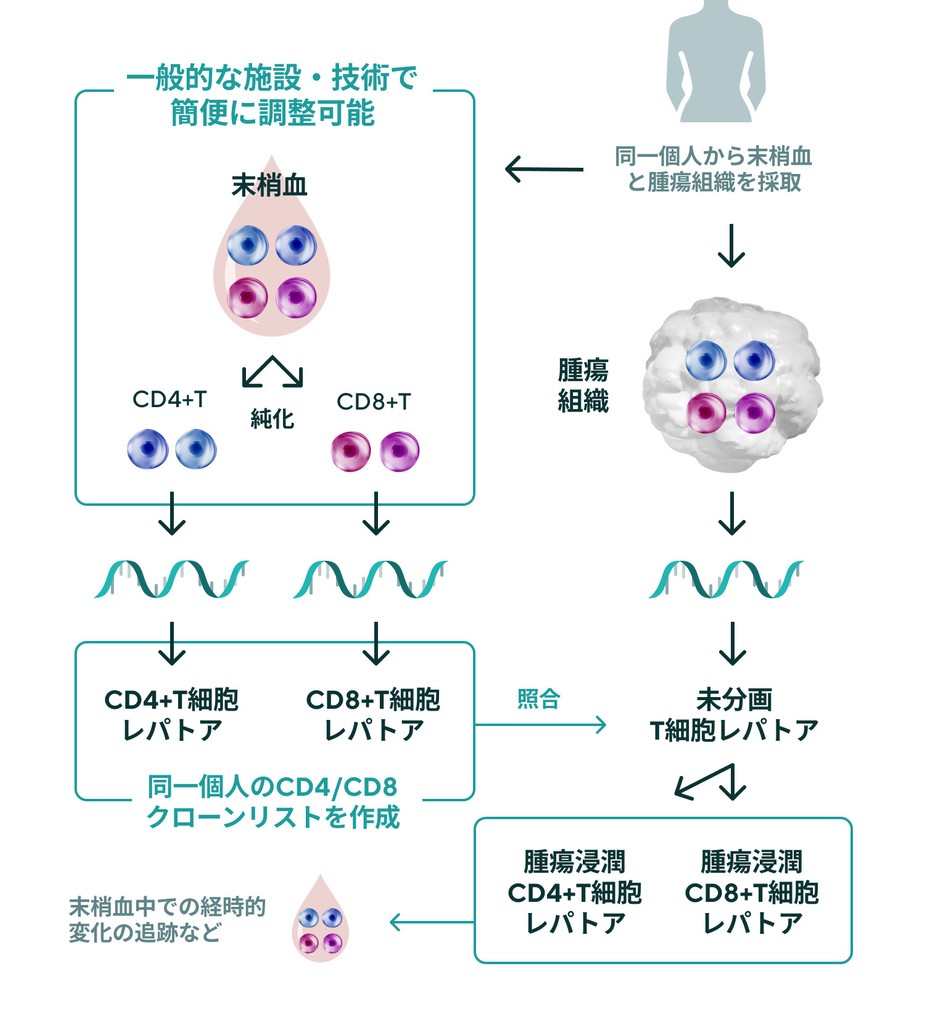
Fractionation of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells is critical for TCR repertoire analysis. On the other hand, purification of T cell subsets from cancer biopsies is technically and time-consuming. IGT has developed a duplicate clone analysis technology that generates a list of clones belonging to CD4 or CD8 based on the TCR repertoire of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood of patients and determines whether the clone present in the TCR repertoire of unfractionated tumor tissue is CD4 or CD8. (patent pending).
This duplicate clone analysis technology allows for easy analysis of changes in tumor-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell clones before and after treatment or over time.
* Fractionation options for CD4 and CD8 T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells are also available.
Peripheral blood TCR analysis by other companies' conventional methods
Tumor-associated T cells are only present in a small portion of the peripheral blood, making difficult to assess.
TCR analysis fpr peripheral blood and tumor duplication by IGT
Any facility can send peripheral blood and tumor biopsies collected at diagnosis to sent to IGT to evaluate specific anti-tumor T-cell responses.
Conventional tumor-infiltrating T-cell leptorenalysis
Simple but not immunologically interpretable.
Time and special techniques are needed to enable immunological interpretation.
Tumor and peripheral blood duplicate clone analysis technology for
versatile tumor-infiltrating CD4/CD8T cells repertoire analysis
Single TCR Repatoir Analysis
By integrating scRNA-seq and TCR repertoire analysis, gene expression information and TCRα/β pair sequences necessary for clone reconstitution can be simultaneously analyzed for individual T cells. Based on the characteristics and frequency of each clone, it is possible to narrow down clones that are promising for TCR gene therapy and other applications.
・
The single-cell RNA-seq performed in this analysis is targeted sequencing using BD's Immune Response Panel, with the option of adding genes related to regulatory T cells, exhausted T cells, etc. Regulatory T cells, exhausted T cells, etc. can be added as an option.
・
Up to 20,000-30,000 cells/analysis; pairing efficiency of mouse and human TCRα/β is about 20%-80% (depending on cell activation state)
・
Simultaneous analysis with protein using BD's Abseq, BioLegend's TotalSeq, etc. is also available
TAS-Seq2 detects about 3 times more genes than BD's WTA kit
TAS-Seq2 has a higher T-cell receptor pairing rate than BD's WTA kit
Example of analysis of tumor-infiltrating CD8⁺T cells in a B16F10 subcutaneously implanted tumor mouse model upon anti-PD-L1 treatment (WTA)
Approx. 50,000 reads/cell
EXPRESSION PATTERNS OF REPRESENTATIVE CD8+ T CELL MARKER GENES
BD WTA
Clusters identified by TAS-Seq2
0: terminally exhausted, 1: effector, 2: proliferated, 3: exhausted progenitor-1, 4: exhausted progenitor-2, 5: naïve-like, 6: stem-like, 7: dying cell
・
TAS-Seq2 can identify CD8+ T cell subsets that are difficult to identify with BD's WTA kit
・
TAS-Seq2 can clearly detect genes involved in the regulation of CD8+ T cell function with a lower drop-out rate